Brazil: A Geographic Large in South America
Associated Articles: Brazil: A Geographic Large in South America
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to Brazil: A Geographic Large in South America. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Brazil: A Geographic Large in South America
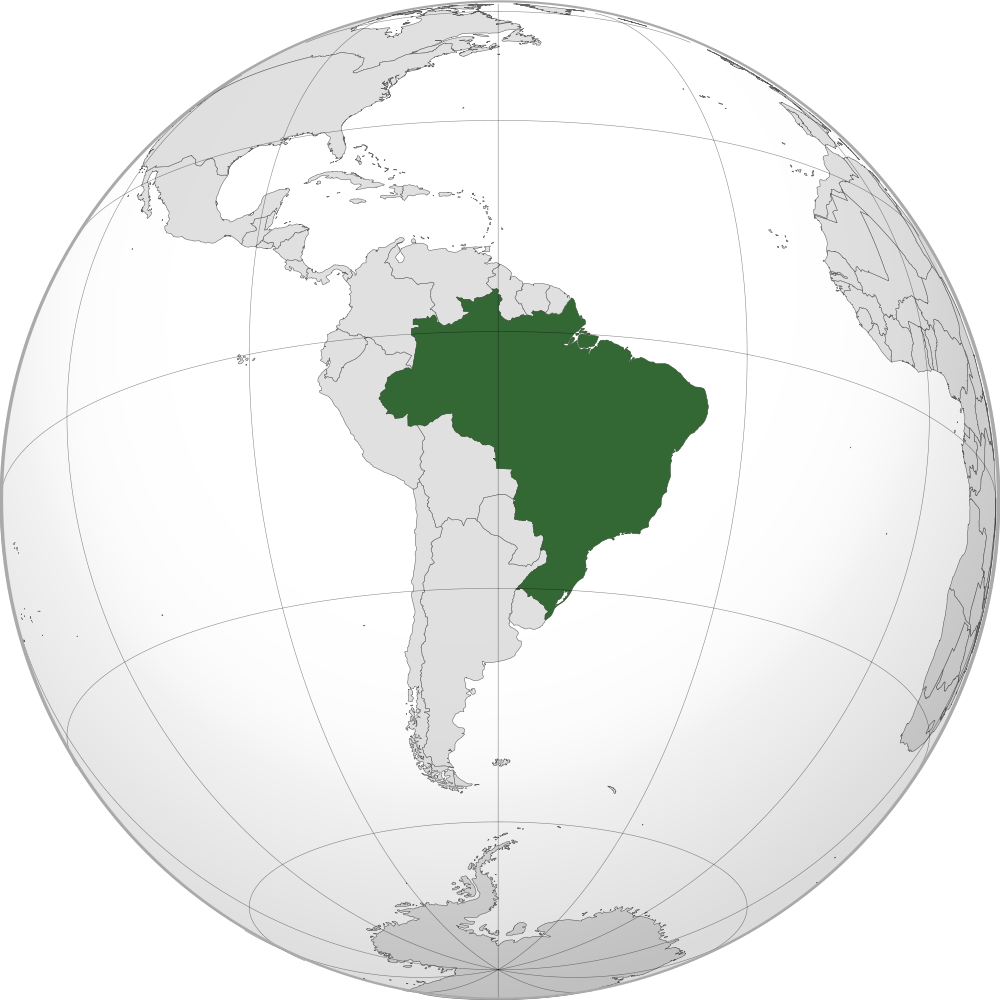
Brazil, the most important nation in South America, boasts a shocking variety of landscapes, climates, and ecosystems. Its huge territory, formed like a large, barely tilted parallelogram, dominates the japanese half of the continent, extending from the Amazon rainforest within the north to the subtropical grasslands of the south. Understanding Brazil’s geography is essential to comprehending its wealthy biodiversity, its complicated historical past, and its vital function within the world enviornment. This text explores the geographical options of Brazil, inspecting its regional variations and the affect of its distinctive location on its tradition and financial system.
A Continent Inside a Nation:
Brazil’s sheer dimension is staggering. Protecting roughly 8.5 million sq. kilometers (3.3 million sq. miles), it encompasses nearly half of South America’s landmass. This huge expanse ends in a outstanding variety of geographical options, starting from the world’s largest rainforest to expansive savannahs, towering plateaus, and a prolonged Atlantic shoreline. This inside variety contributes considerably to the nation’s cultural mosaic, with distinct regional identities formed by the native surroundings.
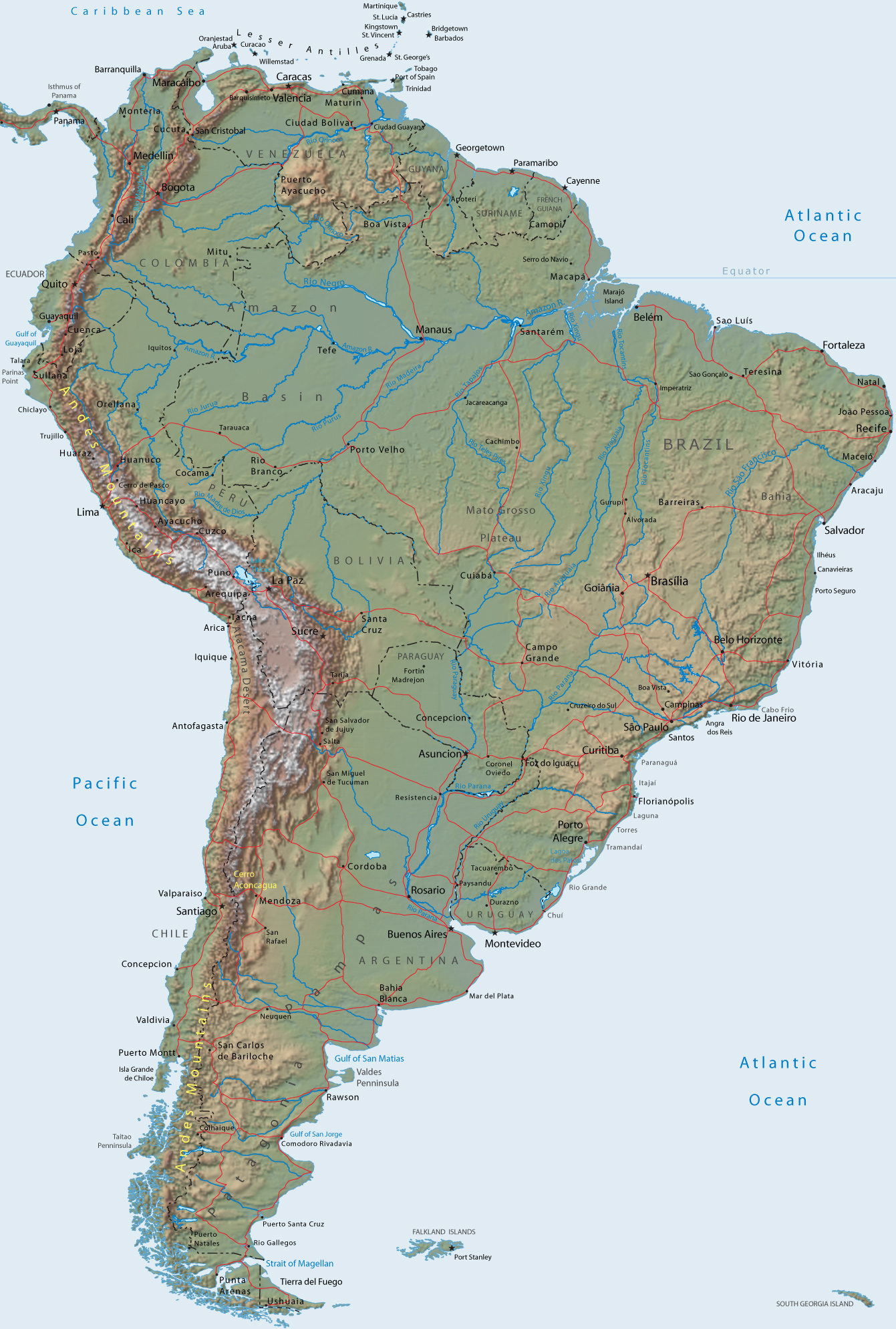
The Amazon Basin: The Coronary heart of Brazil:
The Amazon rainforest, a worldwide treasure trove of biodiversity, dominates the northern a part of Brazil. Protecting roughly 60% of the nation’s territory, this immense ecosystem performs a crucial function in regulating world local weather patterns and harbors an unparalleled array of plant and animal species. The Amazon River, the world’s largest river by quantity, meanders via the guts of the rainforest, creating a fancy community of tributaries and wetlands. This area presents distinctive challenges and alternatives for Brazil, balancing the necessity for sustainable growth with the crucial of preserving this irreplaceable pure useful resource. Deforestation, pushed by agricultural growth and logging, stays a big environmental concern.
The Cerrado: A Treasure Trove of Biodiversity:
South of the Amazon lies the Cerrado, an unlimited tropical savanna characterised by a mosaic of grasslands, woodlands, and gallery forests. Typically ignored in comparison with the Amazon, the Cerrado is remarkably biodiverse, housing a singular array of plant and animal species tailored to its distinct local weather. The Cerrado is an important agricultural area, producing vital portions of soybeans, corn, and cattle, however intensive agriculture has led to vital habitat loss and environmental degradation. Balancing agricultural manufacturing with conservation efforts is a crucial problem for this important ecosystem.
The Pantanal: The World’s Largest Wetland:
Additional south, nestled between the Cerrado and the Andes Mountains, lies the Pantanal, the world’s largest tropical wetland. This seasonally flooded plain helps an unimaginable abundance of wildlife, making it a globally vital biodiversity hotspot. The Pantanal’s distinctive ecosystem is extremely delicate to environmental modifications, and sustainable tourism and conservation efforts are essential for its preservation.
The Atlantic Forest: A Fragmented Jewel:
Alongside Brazil’s japanese coast stretches the remnants of the Atlantic Forest, as soon as an unlimited and steady ecosystem. Intensive deforestation over centuries has lowered the forest to fragmented patches, making it some of the threatened biodiversity hotspots globally. Regardless of its diminished dimension, the Atlantic Forest continues to harbor a outstanding array of endemic species, highlighting the significance of conservation efforts to guard its remaining fragments.
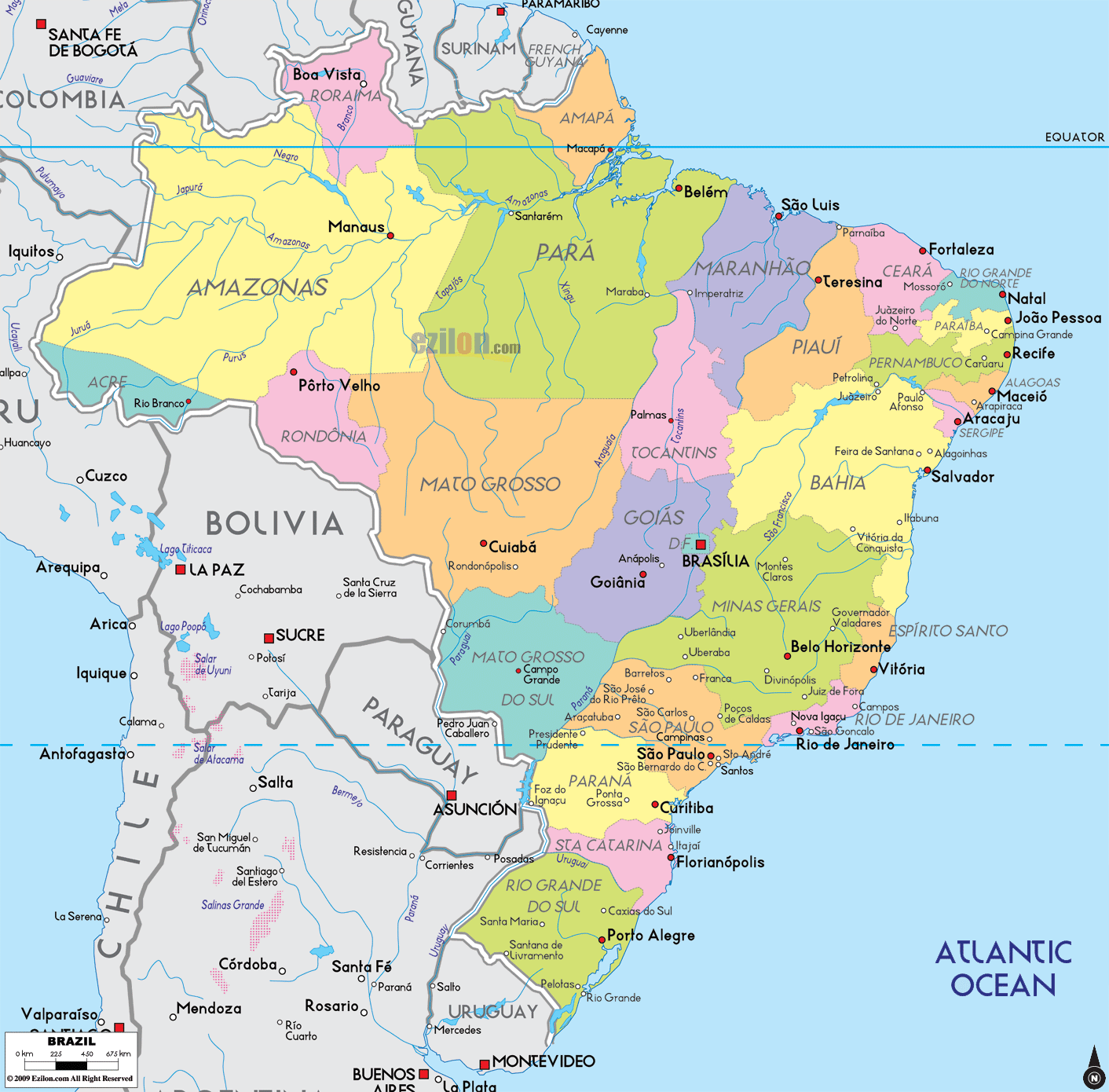
The Brazilian Highlands: A Numerous Plateau:
A lot of Brazil’s inside is dominated by the Brazilian Highlands, an unlimited plateau that rises step by step from the coastal plains. This plateau is characterised by a various vary of landscapes, together with rolling hills, deep valleys, and intensive grasslands. The highlands are wealthy in mineral assets, together with iron ore, manganese, and bauxite, contributing considerably to Brazil’s financial system. Nevertheless, mining actions can have vital environmental impacts, requiring cautious administration and sustainable practices.
The Coastal Plains and Seashores:
Brazil’s intensive shoreline, stretching over 7,400 kilometers (4,600 miles), is characterised by quite a lot of seashores, from the bustling city shores of Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo to the pristine sands of the Northeast. The coastal plains help a various vary of ecosystems, together with mangroves, coastal forests, and sand dunes. Coastal areas are essential for tourism, fishing, and maritime transport, however they’re additionally weak to coastal erosion and air pollution.
Regional Variations and Cultural Range:
Brazil’s various geography has profoundly formed its regional identities and cultural expressions. The Amazon area, as an illustration, is house to indigenous communities with distinctive traditions and life intently intertwined with the rainforest. The Northeast, with its semi-arid local weather and historical past of sugar cane plantations, has a definite cultural heritage mirrored in its music, delicacies, and structure. The South, with its European affect and temperate local weather, possesses a unique cultural panorama in comparison with the tropical north.
Geopolitical Implications:
Brazil’s geographical place can also be essential to its geopolitical function. Its huge territory and various assets make it a big participant in South American and world affairs. Its Amazon rainforest performs a crucial function in world local weather regulation, making Brazil a key actor in worldwide efforts to fight local weather change. Its intensive shoreline offers entry to important maritime routes, strengthening its place in worldwide commerce.
Challenges and Alternatives:
Brazil faces vital geographical challenges, together with deforestation, water shortage, and soil erosion. These environmental points are exacerbated by fast urbanization and financial growth. Nevertheless, Brazil additionally possesses immense alternatives. Its huge pure assets, its strategic location, and its massive and various inhabitants current vital potential for sustainable financial progress and growth.
Conclusion:
Brazil’s map is a testomony to its geographical richness and complexity. From the plush Amazon rainforest to the huge Cerrado savanna and the expansive Atlantic shoreline, Brazil’s various landscapes have formed its tradition, its financial system, and its function on this planet. Understanding this geographical variety is important for appreciating the nation’s distinctive character and addressing the challenges and alternatives that lie forward. Balancing the necessity for financial growth with the crucial of environmental safety might be essential for making certain a sustainable future for this large of South America.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into Brazil: A Geographic Large in South America. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!